Java byte type.
Information
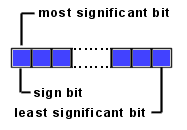
Byte types are so called signed two-complement numbers.
The 2 complement scheme allows both positive and negative integers to be represented.
The most significant bit of a two complement number is its sign bit.
The sign bit is 1 for negative numbers and 0 for positive numbers and for 0.
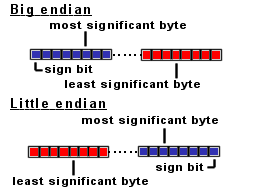
In Java the bytes are big-endian ordered, which means the most significant BYTE (where the sign bit is located) is always on the left side:
Byte values are stored in 1 byte and contains positive or negative integer numbers.
The byte value range is: 28 = 256
Half of this number (256) are positive numbers ranging from: >=0 and <=127
For example:
0x00 = 0
0x01 = 1
0x7F = 127
The other half are negative numbers ranging from: >=-128 and <0
For example:
0xFF = -1
0x80 = -128
To convert negative decimal values into hexadecimal values:
value = 28 + (neg_dec_value)
value = 256 + (neg_dec_value)
For example:
neg_dec_value= -1
value = 256 + (neg_dec_value) = 256 + (-1) = 255
The new decimal value 255 equals 0xFF (Use your Windows calculator, to verify this).
During arithmetic operations the JVM always convert the byte value into an int.
|